
Over 2022, the number of Internet users increased by 1.9 per cent to just under 60 per cent of the global population at the start of 2023. Isn't that an impressive figure? Have you ever wondered how the Internet as a whole works?
Given the interest in this topic, we have decided to devote a separate article to it, in which we tell you what the Internet is, how it is organised and what role ISPs play.
How the Internet works
From a technical point of view, the term «Internet» refers to a structure that combines Internet hardware and software. This structure consists of 3 elements: cables, routers and networks.
Cables
Our entire planet, except Atlantis, is covered with optical cables connecting small networks through special gateways. Some of these cables even run underwater, which makes it possible to cover long distances (for example, the Atlantic Crossing 1 cable, which connects the US to Europe, is 14,000 kilometres long). You can see how it looks like on the maps of submarine and land cables.
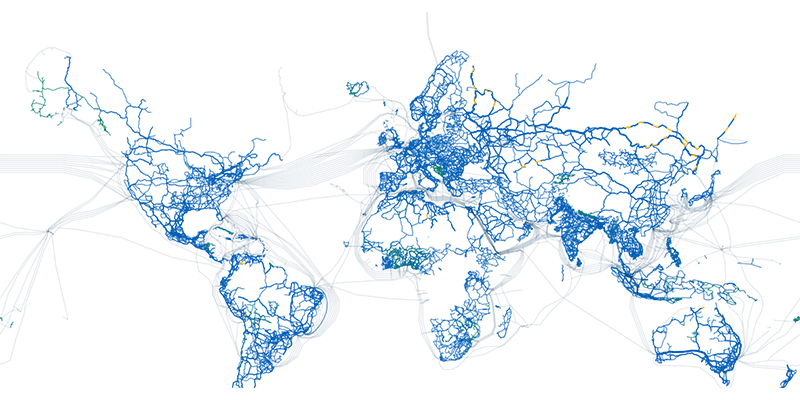
Thus, an Internet network is a multitude of fibre optic cables that are responsible for transmitting data from one network to another in the form of optical signals.
Routers
Routers are those devices that send information between access points (from one computer to another). Their function is to choose the fastest and most reliable route possible.
Networks
All devices are connected to them in order to access the Internet. Devices that are part of the same local area network (LAN) exchange data without problems. But data exchange outside of networks is supported by an Internet Service Provider (ISP). The following is a detailed discussion of ISPs.
Who are Internet Service Providers and what tasks do they perform?
Internet service providers are companies whose main activity is aimed at providing the client with access to the Internet network. They are an integral link in the process of Internet distribution and act as intermediaries between the communication channels of the global network and end consumers.
Among the functions that an Internet Service Provider performs are:
- Connecting to the global Internet using various data transmission technologies.
- Providing unique IP addresses to users to identify their devices on the network.
- Providing data transfer between users and websites. This includes downloading and sending data, browsing the web, using email, messaging, etc.
- Providing a certain data transfer rate depending on the service package selected by the user.
- Providing technical support to subscribers on connection and configuration of equipment, solving technical problems, etc.
- Provision of privacy and security (protection from hacker attacks and malicious programmes, protection of user data privacy).
- Provision of additional services (TV, hosting, Internet telephony, etc.).
- Development of own network and infrastructure to ensure stable and fast Internet connection.
The history of the World Wide Web dates back to the 1960s with the introduction of the packet switching model to the world. At this stage, access to the Internet was provided through dial-up connections using a telephone line, so even with very slow connection speeds, it was impossible to make calls in parallel.
In the early 2000s, high-speed (broadband) Internet access was already available thanks to the introduction of DSL technology. During the following years and up to today, technology has improved, as a result of which the world has seen cable and satellite Internet and fibre optic communication lines.
Classification of Internet providers or where the Internet comes from
All Internet service providers on the telecom market today can be divided into 3 groups:
- Tier-1 Internet service providers.
These companies own intercontinental cables and exchange traffic among themselves for free. They earn their money mainly by providing transit services to Tier-2 ISPs. Smaller Internet companies also turn to Tier-1 providers when they need to transmit information over long distances. - Tier-2 Internet Service Providers.
These are usually national operators at the level of a country or a group of countries in a particular region that sell cables and other network equipment to Tier-2 ISPs. The process of such companies cooperating with each other is called peering. Fast peering is enabled by so-called Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) located around the world. These are premises and buildings with a bunch of PCs and routers that connect several Internet service providers. In total, there are about 240 such locations in the world today. - Tier-3 Internet Service Providers.
These include small regional companies that sell Internet connections to end consumers. They either buy Internet for resale from Tier-2 operators or exchange free parity connections with each other directly or at traffic exchange points with other Tier-3 providers.
A visualisation of the development of the Internet over the period 1997-2021 is presented in the video:
Depending on the technologies used, ISPs can be categorised into those that:
- Provide broadband access to the World Wide Web on the basis of FTTB (ETTH) — the most common technology today using twisted pair cable, which can provide speeds of up to 1 Gbps/s.
- Connect the Internet using the most progressive xPON technology — providing a gigabit connection using a special optical cable.
- Provide 3G / 4G / LTE mobile Internet — users access the Internet from their smartphones, which is very convenient, but with limits. The speed limit of the latter LTE technology is 300 Mbps (actually it is lower than the declared speed).
- Provide wireless communication based on Wi-Fi and WiMax — the Wi-Fi module built into the prevailing majority of modern devices allows to establish a stable Internet connection within a certain area.
- Organise satellite communications — one-way (asymmetric), which uses a satellite to receive information and conventional communications to transmit data, or two-way (symmetric), which allows Internet access anywhere in the world.
What does the ISP charge for?
If you think that you pay the ISP only for the use of leased lines, you are mistaken. The amount of the payment is based on the cost of creating a fibre optic network, purchasing special equipment for signal amplification and switching devices, as well as their maintenance.
It also matters how the network is designed and its capacity, the availability of backup backbones and generators, and the technologies used. And also do not forget that the Internet tariff includes the company's expenses for utilities, rent and maintenance of office space, staff salaries. Depending on these features, the cost of Internet service differs from provider to provider.
Can the Internet be blocked?
Many users wonder whether the Internet can be blocked within the country. Well, no: it is very difficult to completely shut down the Internet, as it is a global network. But it is possible to restrict access to the network (for example, as it was in Belarus after the mass protests in August 2020). But even such a partial blocking is very expensive for the country (for example, in the same Belarus the losses amounted to $56 million per day). Can you imagine what losses the state would incur in case of disabling not only websites and services undesirable to the ruling regime, but also the entire infrastructure system (banks, railways, etc.)?
However, attempts to completely control the Internet by digital dictatorships take place all over the world. And they are increasing every year: while in 2020 there were 159 shutdowns in 29 countries, in 2021 there were already 182 shutdowns in 34 countries. So it is not surprising that, in light of these trends, there is continued talk in some countries about creating localised Internet networks.
How to choose an ISP
When choosing an ISP, it is worth understanding that you have a long-term «relationship» with it ahead of you. Therefore, it is important to pay attention to the following criteria:
- Connection technology: depending on your location, different connection technologies from providers may be available.
- Connection quality: bandwidth should be sufficient to fulfil the tasks you need (browsing sites, downloading large files, holding online conferences, etc.).
- Possibility to choose a tariff plan acceptable for you from among those offered.
- Availability of provider coverage at your address.
- Opportunities to provide additional services.
- Stable work in the market and positive reputation.
Maxnet company is ready to become your reliable Internet provider, as well as to connect other types of services on request. If you have any questions, you can consult our specialists by phone number 0800-31-0700.
Еще комментарии








Олександр
17.08.2023
1
0
Reply
Макснет
18.08.2023
0
0
Reply