
To get speeds in excess of 100 Mbit/s you need a transmission environment that enables you to achieve these speeds. Here's how to check that your equipment is suitable for it.
The ability of devices to operate at high speeds is affected by factors that can be roughly divided into 2 categories:
- Passive section of the network (cable, connectors).
- The active section of the network (router, PC network card).
How to check the capacity of your equipment on the passive section of the network
- To ensure bandwidths above 100 Mbit/s, the twisted pair cable must be 8-wire throughout the connection section. By connection section we mean:
- with Ethernet technology: the section from the provider's switchboard to your equipment;
- with GPON technology: the section between the ONU terminal and the router or PC.
You can check which cable goes through your flat by disconnecting the connector from the router and looking at the number of wires (there may be 4 or 8).


- If the cable is 4-wire, it will need to be replaced by an 8-wire cable.
Note that the crimping of the connectors must also be done properly. There are cases when it deteriorates over time due to constant manipulation of the cable. This results in poor connection quality and loss of any speed.
Residents of apartment buildings need to keep in mind the following: if the cable used to be rewired during the transition from one provider to another, there may be an 8-wire twisted pair in the flat and a 4-wire pair in the entryway. If necessary, our support staff can help you with this diagnosis.
Once you have sorted out the passive section check, you need to ensure that your devices are able to operate at increased speeds.
How to check the capacity of your equipment on the active section of the network
Today, most routers and NICs on computers and laptops have an Ethernet interface (twisted pair connector) of 100 Mbit/s or 1000 Mbit/s. The most expensive models can have 2500 Mbit/s. All standards can also operate at lower speeds, selecting the standard of the "weakest" device (e.g. a 1000 Mbit/s PC with a 100 Mbit/s router will operate at 100 Mbit/s).
Note: If you are on GPON technology, all subscriber terminals we provide have a 1000 Mbps Ethernet port.
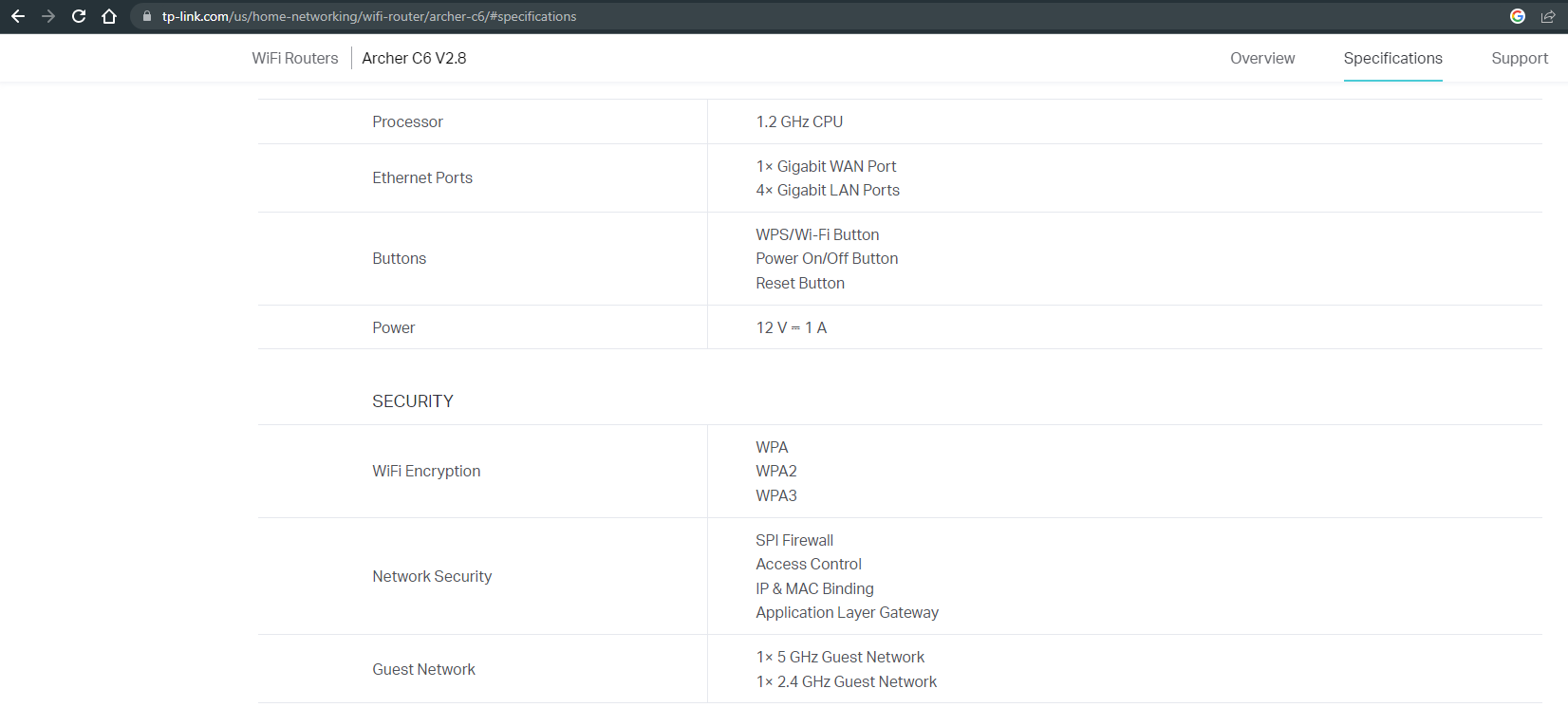
Also, to check if the router is suitable, you need to determine exactly what the WAN speed of the Ethernet port is. Because no matter what technology you are connected with, the router will be connected exactly by twisted pair (from our switch, if Ethernet, or from the terminal, if GPON). The easiest way to check this is to go to the manufacturer's official page and see the specifications of a particular model.
Important: it is the WAN speed you need to check, not the Wi-Fi speed.
Using the TP-Link Archer A6 router as an example, you can see that there is 1 Gbps WAN support:
You can check your PC's network card in the adapter's properties.
If you have Windows installed on your device, you must:
- Go to "Search" - "Device Manager".
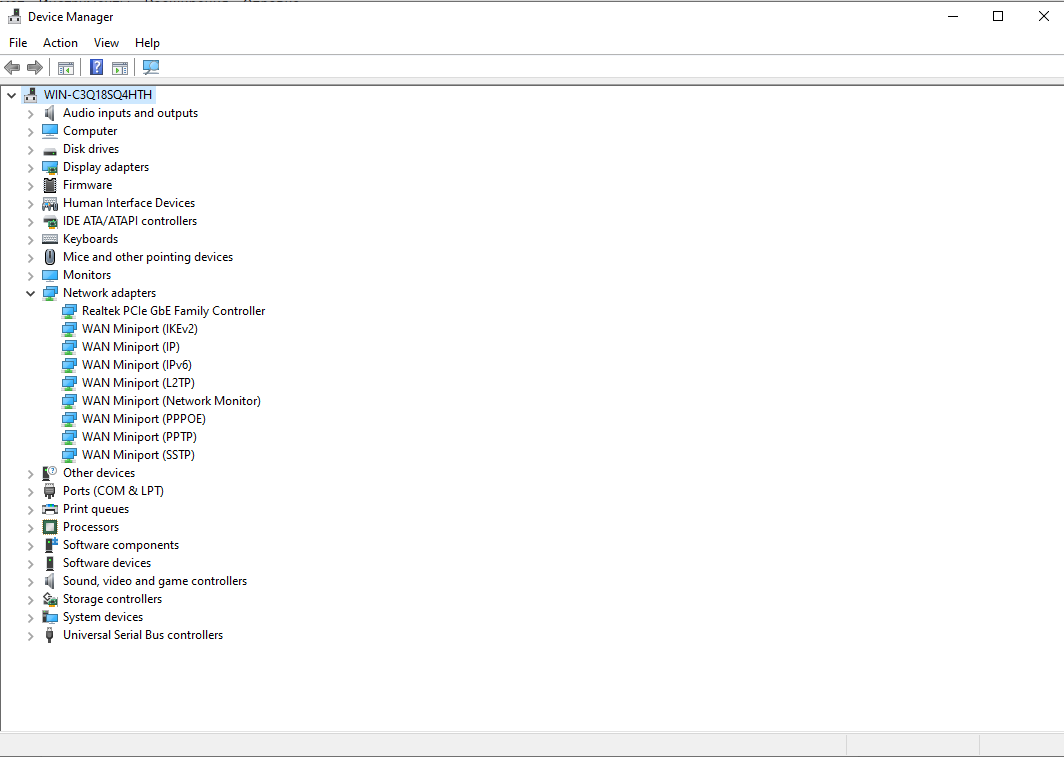
- In network devices, select "Ethernet" - "Adapter status". Note the name right away: if Gigabit Ethernet or GbE is specified, the speed of the network card is 1000 Mbit/s, if Fast Ethernet, it is 100 Mbit/s.
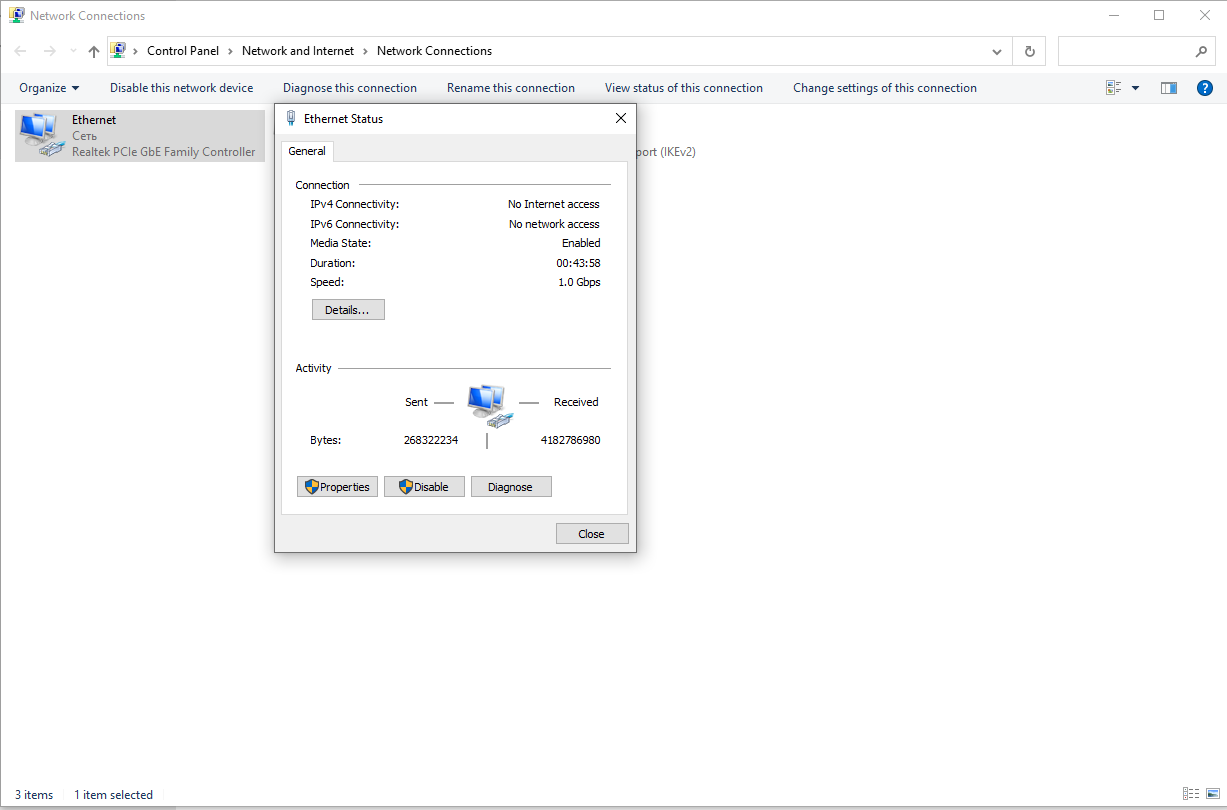
- If it is not clear from the name, you should open "Properties" - "Advanced" - "Speed & duplex". If it is possible to select 1 Gbit/s, the card is suitable (in this case "Auto Negotiation" of the duplex should be left).
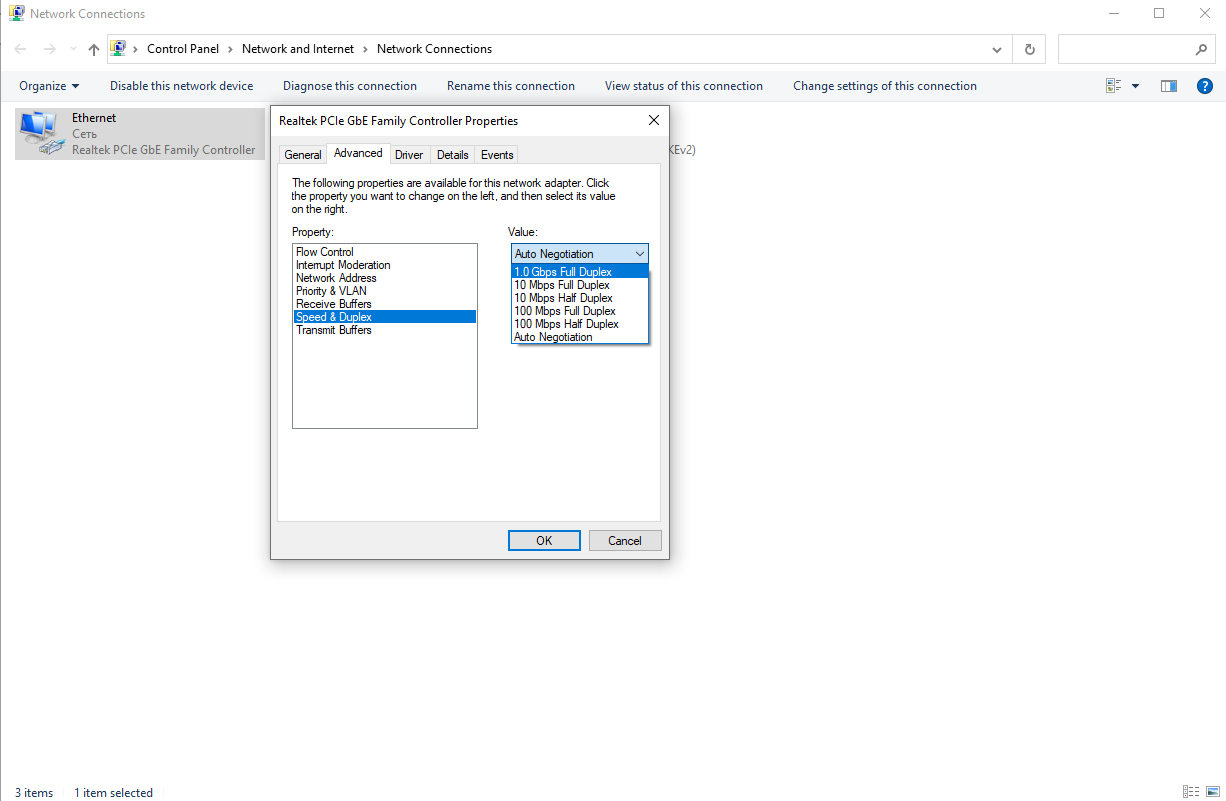
- If both the router and the PC with 1000 Mbps interfaces are connected with an 8-wire twisted pair, the connection status on the PC will show the corresponding network status. To find out, press “Start” - “Settings” - “Network and Internet” – “Properties”.

To check devices on Linux, the procedure is as follows:
- Open a terminal with alt+ctrl+t and enter the command "ip link show" to find out the name of the interface on the system.
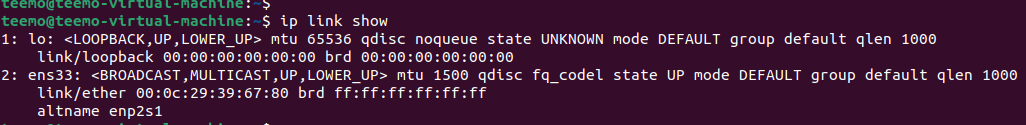
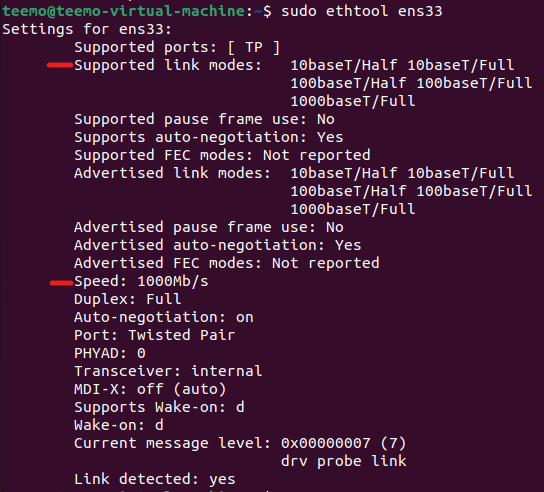
- Next use the "ethtool" utility to view the properties of the desired network card and its current status.
From the line "Supported link modes" you will find information about the capabilities of the network card. From the "Speed" line you will get information about the current connection status (if you see 1000 Mbit/s, there is nothing wrong between the router, PC and cable).
The result of this check on your NIC will give you an indication of whether the hardware supports gigabit speeds and whether you need to replace any of the components.
In some cases where updating your NIC is difficult (e.g. if you have a laptop), you may be able to purchase a portable USB adapter with gigabit Internet support to quickly upgrade to higher speeds.
Еще комментарии








DM
05.06.2023
7
0
Reply